VCRS(Vapour Compression Refrigeration System)- Working Principle, COP Formula, PV, TS Diagram, so far I have shared information about different cycles in refrigeration system, in the last article I have shared information about Bell Coleman Cycle.
What is VCRS Cycle?
In this type of refrigeration cycle we used refrigerant like NH3, R11, R-12, R-34(eco friendly because chorine free) which circulated through the cycle, there are mainly four devices we have lets start with compressor, condenser, expansion device and evaporator.
Evaporator absorb heat from the system and give us desire cooling at the system which needed by us.
We can also say that it is the improved type of refrigeration system than air refrigeration system, most of the time we used this refrigeration system in domestic as well as industrial purpose.
Here, we will study theoretical vapour compression cycle.
Assumptions of Theoretical Vapour Compression Refrigeration System-
- Entry to the compressor is saturated vapour.
- Exit of condenser is saturated liquid.
Working of Vapour Compression Refrigeration System-
For proper understanding working of this cycle we need to look at block diagram of this cycle(note- block diagram can be clock wise as well as anti-clock wise because refrigeration cycle works in the anti-clock wise direction as we see in PV as well as TS diagram).
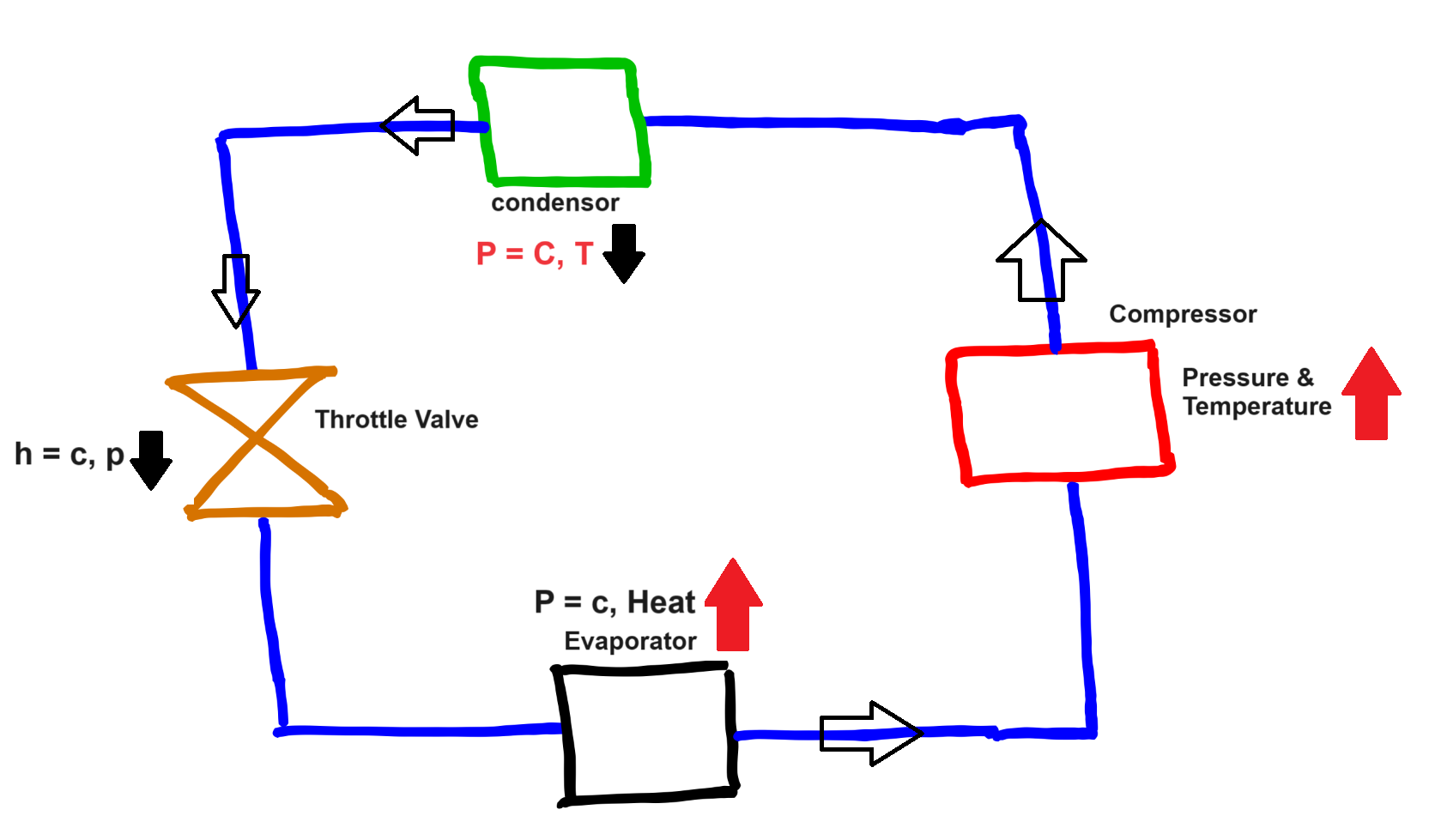
In this cycle we have four process, we will discuss one by one-
Compression Process(1-2)- This process is also known as reversible adiabatic process or isentropic compression. In this process pressure and temperature of refrigerant both increased
Condensing Process(2-3)- This process is also known as Isobaric heat rejection by maintaining constant pressure.
At constant process, heat is rejected by the refrigerant that is why temperature decreases.
Expansion Process(3-4)- It results a decrease in pressure, device we used is throttle valve.
This process is also known as isenthalpic expansion process means enthalpy is remain constant.
Vapourising Process(4-1)- In this process heat absorbed from the system at constant pressure in other words we can also say heat is supplied at constant pressure.
PV & TS Diagram of Vapour Compression Refrigeration System-
Below, I have shared PV and TS diagram of VCR cycle, which is helpful to understand about all the processes better way.
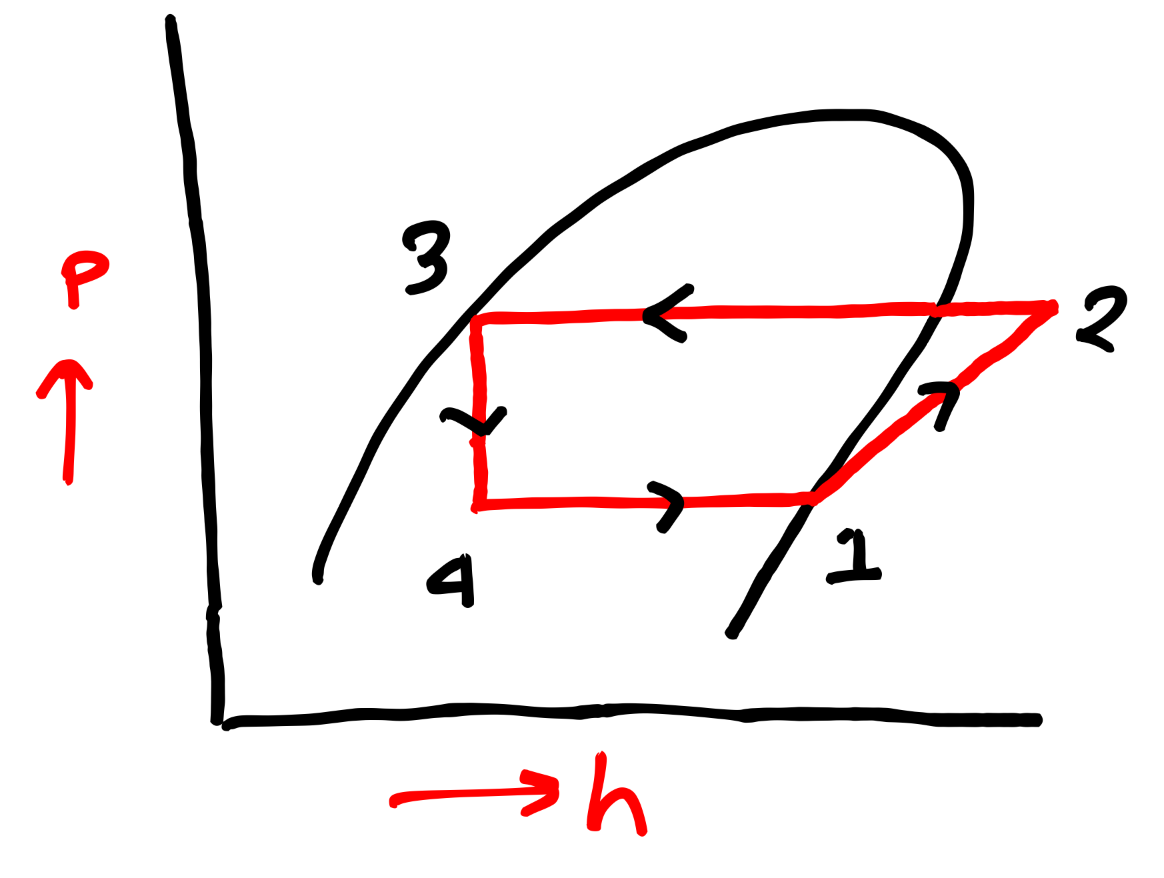
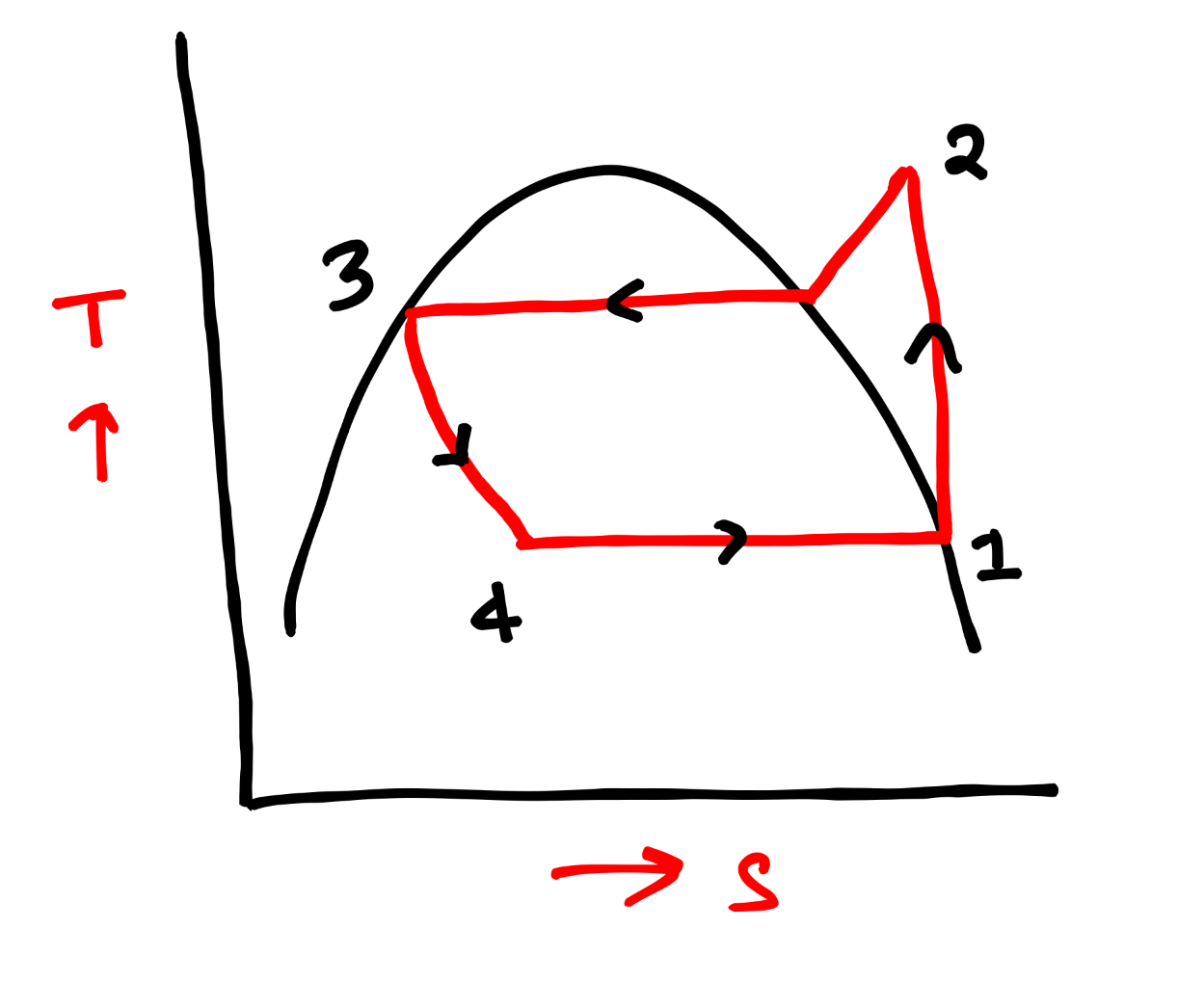
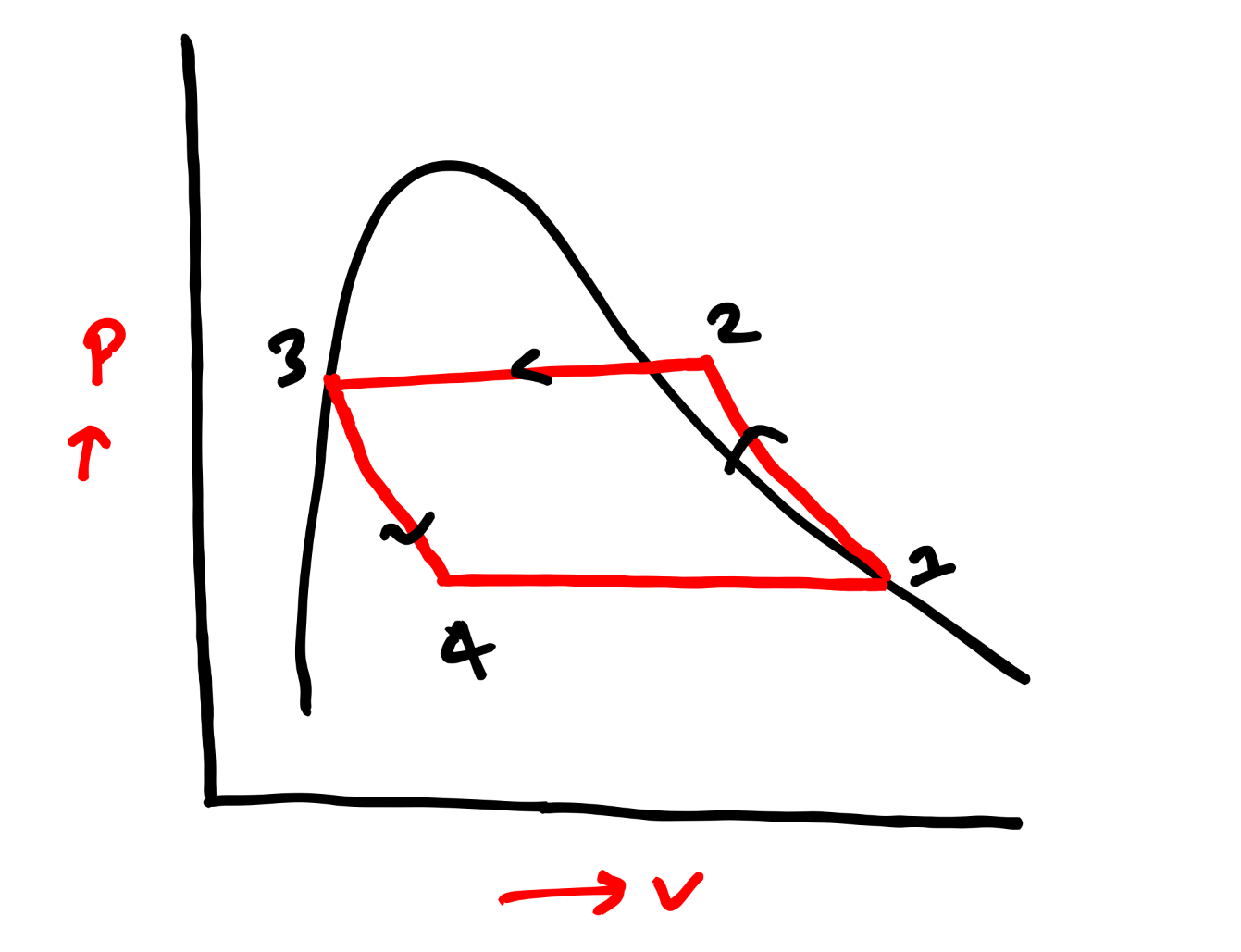
COP Formula of Vapour Compression Refrigeration System-
COP(Coefficient of performance) of VCRS = Desire Effect/Workinput
I have shared few key points in the below section, there refrigeration effect I have mention its other name is Desire effect in case of refrigeration system.
So, COP = RE/Work input = (h4 – h1)/(h2 – h1)
Like efficiency, COP is also dimension less.
Pros and Cons of VCRS Cycle-
It is having advantages of VCRS are-
- Running cost is low.
- Its COP is high
- Size is small if we will compare with air refrigeration cycle
- It can be use for different range of temperature
disadvantages of VCRS are-
- Initial capital investment is high
- Many refrigerants cause ozone depletion those refrigerants having chlorine element like CFC refrigerant.
- Difficult to control leakage problem because of high pressure and temperature of refrigerant in the cycle due to compressor.
Keys Facts of VCRS Cycle-
- Refrigeration effect(R.E) = (h1 – h4)KJ/Kg
- Refrigeration Capacity = m* x RE KJ/Sec or KW
- Work Input(Win) = (h2 – h1) KJ/kg, Power = m* x Win kJ/sec or KW
FAQ’s of VCRS-
Q.1 What is the Working Principle of VCRS?
Answer- It is system in which refrigerants circulates through four different components, where four processes takes place which help us to get desire effect(i.e. cooling) at our system.
Q.2 What do you mean by VCRS?
Answer- VCRS stands for vapour compression refrigeration system, which used in domestic as well as commercial purpose for refrigerating effect. In this refrigerant circulates in a closed cycle.
Q.3 What is the 4 process of VCRS?
Answer- Here are four processes of VCRS cycle, compression, condensation, expansion and evaporation.
Vapour Compression Refrigeration System MCQ’s SSC JE/GATE/ESE Exams-
In this section, you will get MCQ’s asked in different exams like SSC JE, Other exams, GATE, ESE exams as well.
So, lets get started with all questions-
Question 1: In a Vapor Compression Refrigeration System, which component is responsible for compressing the refrigerant vapor?
a) Condenser b) Compressor c) Evaporator d) Expansion valve
Solution 1: b) Compressor
Question 2: What is the primary function of the evaporator in a VCRS cycle?
a) To compress the refrigerant b) To remove heat from the refrigerated space c) To expand the refrigerant d) To reject heat to the surroundings
Solution 2: b) To remove heat from the refrigerated space
Question 3: During which phase of the VCRS cycle does the refrigerant absorb heat from the surroundings?
a) Compression b) Condensation c) Expansion d) Evaporation
Solution 3: d) Evaporation
Question 4: What is the role of the expansion valve in the VCRS cycle?
a) To increase the pressure of the refrigerant b) To control the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator c) To remove heat from the refrigerated space d) To compress the refrigerant vapor
Solution 4: b) To control the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator
Question 5: In the T-s (Temperature-entropy) diagram of the VCRS cycle, which process corresponds to the isentropic compression of the refrigerant?
a) Process 1-2 (Isentropic Compression) b) Process 2-3 (Constant Pressure Heat Rejection) c) Process 3-4 (Isentropic Expansion) d) Process 4-1 (Constant Pressure Heat Absorption)
Solution 5: a) Process 1-2 (Isentropic Compression)
Question 6: The specific heat of a material is given as 0.5 kJ/kg⋅°C. If a 2 kg mass of this material is heated from 20°C to 60°C, calculate the heat transfer. (Take �=��Δ�)
a) 40 kJ
b) 50 kJ
c) 60 kJ
d) 70 kJ
Solution 6:
=2 kg×0.5 kJ/kg⋅°C×(60 °C−20 °C)
Therefore, the correct answer is (a) 40 kJ.
Question 7: A steam engine receives 5000 kJ of heat and produces 2000 kJ of work. Calculate the heat rejected by the engine. (Take )
a) 3000 kJ
b) 5000 kJ
c) 7000 kJ
d) 9000 kJ
Solution 7:
Δ
Therefore, the correct answer is (a) 3000 kJ.
Question 8: If a force of 500 N is applied to move an object a distance of 10 meters, calculate the work done. (Take )
a) 50 J
b) 500 J
c) 5000 J
d) 50000 J
Solution 8:
Therefore, the correct answer is (c) 5000 J.
Question 9: A gas expands from an initial volume of 2 m³ to a final volume of 6 m³ against a constant pressure of 100 kPa. Calculate the work done by the gas. (Take )
a) 400 kJ
b) 800 kJ
c) 1200 kJ
d) 1600 kJ
Solution 9:
Therefore, the correct answer is (a) 400 kJ.
Question 10: If the efficiency of a heat engine is 0.6 and it absorbs 3000 kJ of heat, calculate the work done by the engine. (Take )
a) 1200 kJ
b) 1800 kJ
c) 2400 kJ
d) 3000 kJ
Solution 10:
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) 1800 kJ.
Question 11: A water pump lifts 500 kg of water from a well to a height of 20 meters. Calculate the gravitational potential energy gained by the water. (Take , where )
a) 98,000 J
b) 98,000 N
c) 980 J
d) 980 N
Solution 11:
Therefore, the correct answer is (a) 98,000 J.
Question 12: A car engine absorbs 4000 J of heat and does 3000 J of work. Calculate the change in internal energy of the engine. (Take )
a) 1000 J
b) 2000 J
c) 3000 J
d) 4000 J
Solution 12:
Therefore, the correct answer is (a) 1000 J.
Question 13: A refrigerator has a coefficient of performance (COP) of 4. If it consumes 500 W of electrical power, calculate the rate of heat removal from the refrigerated space. (Take )
a) 125 W
b) 250 W
c) 500 W
d) 2000 W
Solution 13:
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) 2000 W.
Question 14: A steam engine operates between two reservoirs at temperatures of 800 K and 400 K. Calculate the maximum possible efficiency of the engine. (Take )
a) 50%
b) 60%
c) 66.67%
d) 75%
Solution 14:
Converting to percentage, the correct answer is (a) 50%.
Question 15: A pump lifts water from a well at a rate of 0.05 m³/s to a tank located 10 meters above the well. Calculate the power required by the pump. (Take , where and )
a) 4.9 kW
b) 5.0 kW
c) 5.5 kW
d) 6.0 kW
Solution 15:
Power=490 W
Converting to kilowatts, the correct answer is (a) 4.9 kW.
Question 16: A refrigerator consumes 800 W of power and rejects heat to the surroundings at a rate of 1600 W. Calculate the coefficient of performance (COP) of the refrigerator. (Take COP=Heat Removed/Work Input)
a) 0.5
b) 1.0
c) 2.0
d) 3.0
Solution 16: COP=Heat Removed/Work Input
COP=1600 W/800 W
Therefore, the correct answer is (c) 2.0.